Until recently, the use of astringents and toners in dermatology was primarily limited to their anti-acne and astringent properties, although some also functioned as mild antiseptic agents suitable for mild or limited bacterial infections of the skin surface (24). Today soothing toners are increasingly being used by dermatologists and aestheticians for their anti-inflammatory and anti-irritant benefits as part of a post-cosmetic surgery regimen such as laser, chemical peel, or light-modulated procedures. The perceptual attributes of clean and refreshing for oily and acne-prone skins and soothing and calming for dry and sensitive skins in a cosmetically acceptable toner formulation assure patient compliance when compared with traditional drug vehicles that lack the aesthetic characteristics preferred by patients (26).
|
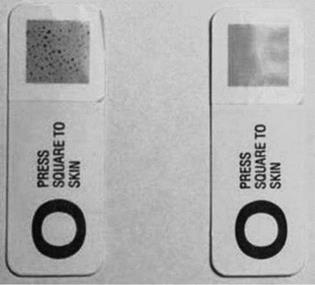
Figure 1 Macroscopic view of Sebutapes taken from oily skin surface before (left) and after (right) toner treatment. The fewer and smaller black spots on the right indicate a reduction in sebum after treating the skin with an oily skin toner. The number of pores and amount of sebum secreted can also be determined via image analysis. |