Tyrosinase activity can be greatly inhibited by cinnamic acid, aloin, and sophorcarpidine, of which sophorcarpidine functions as an uncompetitive inhibitor, compared to aloin and cinnamic acid, which are mixed-type inhibitors (67). Tan et al. (67) demonstrated that
sophorcarpidine, aloin, and cinnamic acid can not only bind to the enzyme, but also to the enzyme-substrate complex as well, leading to the inactivation of tyrosinase.
Chemical structures of some depigmenting agents. Most of the compounds are modulators of melanogenic enzyme activity, their structures show chemical analogy with L-tyrosinase the natural substrate of tyrosinase.
1. Structure of hydroquinone
![]() OH
OH
2. Structure of kojic acid
![]() O
O
I I
OH
O
3.
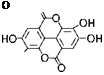 |
Structure of ellagic acid
4. Structure of aloesin
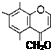 CH2COCH2 HO
CH2COCH2 HO
5.
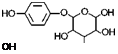 |
Structure of arbutin
6.
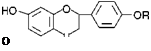 |
Structures of liquiritin and liquirigenin
Liquiritin, R = Glucosyl liquirigenin, R = H.
