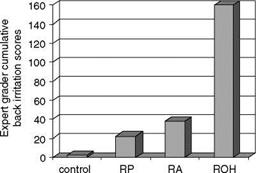
While much of the substantial literature on the improvement of skin wrinkles by topical retinoids is focused on trans-RA, there are also data available on the vitamin A compounds which are used cosmetically. Since retinoids are irritating to skin, defining skin-tolerated doses clinically is a key step in working effectively with these materials. Retinol is better
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
tolerated by the skin than trans-RA (2). In our testing we noted that retinyl propionate is milder to skin than retinol and retinyl acetate (Fig. 2).
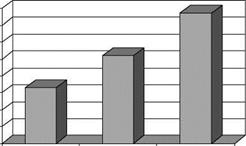
Since retinoids in general tend to be fairly potent, topical doses of less than 1% are generally sufficient to obtain significant effects. At low doses, in double-blind, split-face, placebo-controlled facial testing (12-week duration), both retinol and retinyl propionate have been shown to be significantly effective in reducing facial hyperpigmentation and wrinkles across the study (Fig. 3). Determination of treatment effects was based on quantitative computer image analysis and blinded expert grading of high resolution digital images.
|
|
 |
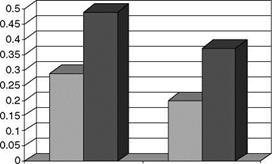
There are also clinical studies published on other retinoids. Retinyl palmitate has very low irritation potential and is effective if tested at a very high dose such as 2% (9). There are also several references describing the clinical efficacy of retinaldehyde, typically at a dose of 0.05% (10-12). However, retinaldehyde has irritation potential similar to retinol (13).