As representative for the vitamin B3 family of compounds, there are several published reports on the diversity of clinical effects of topical niacinamide (14-18). These data
).
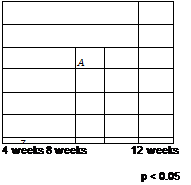
were obtained from double-blind, placebo-controlled, left-right randomized studies. For example, topical niacinamide has been shown to reduce skin fine lines/wrinkling (Fig. 5). The effect increases over time and is significant after eight to 12 weeks of treatment. Topical niacinamide also improves other aspects of aging skin, such as reduction in sebaceous lipids (oil control) and pore size, which likely contribute at least in part to improved skin texture (Fig. 6). Additionally, niacinamide improves skin elastic properties as demonstrated for two parameters of skin elasticity (Fig. 7). Beyond these effects, there is also improvement in appearance of skin color (reduction in hyperpigmented spots and reduced skin yellowing) as noted above. Fairly high doses (2-5%) of vitamin B3 have been used to achieve desired benefits. However, since there is very high tolerance of the skin to niacinamide even with chronic usage, high doses can be used acceptably. In fact, as noted above, since topical niacinamide improves skin barrier, it actually increases the skin’s resistance to environmental insult (e. g., from surfactant) and reduces red blotchiness (Fig. 8).
Some data on myristoyl-nicotinate have been presented (31) to suggest that a similar broad array of benefits occurs with this agent when used topically (1-5% doses). Clinical data for topical nicotinic acid and other esters are not available.
![]()
![]()
![]()
 03
03
Ф _
3 о
I §
st
о – Q ~ a) с о cs
Figure 6 Topical niacinamide improves skin surface texture. Subjects were female Caucasians (n = 50) who applied placebo control versus 5% niacinamide formulations to their faces (12-week, double-blind, split-face, left-right randomized clinical trial).
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
